 Networks
Networks
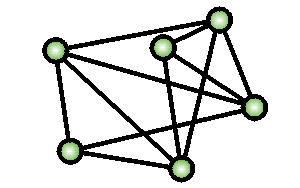
Topology
Point-to-point (mesh)
A lot of wires!

Ring
A ring can provide redundancy.

When a segment fails, the signal can still go around the other way.
 But if several segments fail at the same time ...
But if several segments fail at the same time ...


Bus
Vulnerable to break in bus, but not to failure of nodes.
Used for Ethernet based on old Thickwire (10Base5) or
Thinwire (10Base2) coax cable.

Star
Vulnerable to failure of central node (hub) but not to
failures in individual segments.
Used for Ethernet based on twisted-pair cables (10BaseT and 100BaseT).
Also used for token-ring networks.
Protocols
Competing needs and solutions
- Data vs. voice/video
- Packet switching
- IP vs. ATM
Token ring
Messages circulate around the ring in tokens.
A station wanting to send a message waits until it receives a token
indicating that the network is free.
Token-ring networks don't provide the ring-type redundancy mentioned
earlier
because the token must circulate around the ring.
The 'ring' is usually implemented physically as a star.
Ethernet
A station wanting to send a message listens until the network is
silent, then sends its message. If two stations try sending at the
same time, there will be a collision. Each station then waits
a random time and tries again.
Messages are divided into variable-length
packets up to 1514 bytes long.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM)
Messages are divided into small (53-byte) fixed-length cells. Each
cell can specify a required quality of service and the route
is established before transmission.
Good for both data and voice/video.
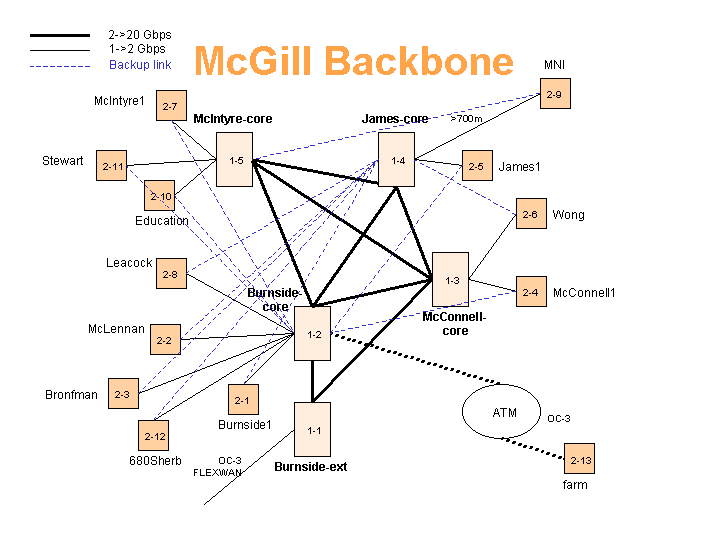
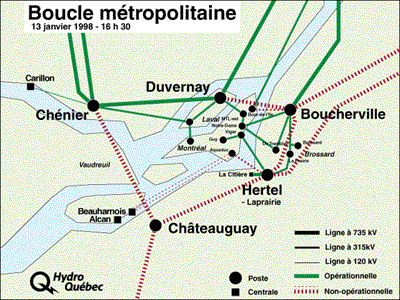
Real world
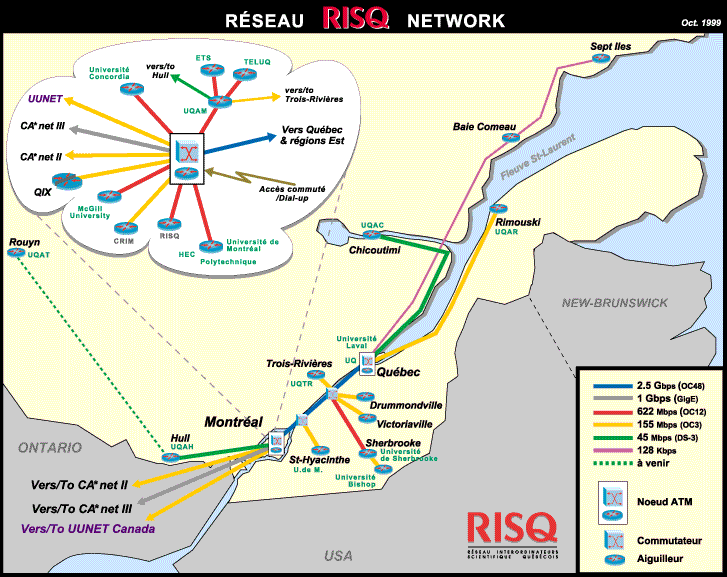
QIX includes RISQ, UUNet Canada, Vidéotron, COGECO, QuébecTel, MLink,
Openface, AT&T Canada - MetroNet, and Bell Nexxia.

Telus national network
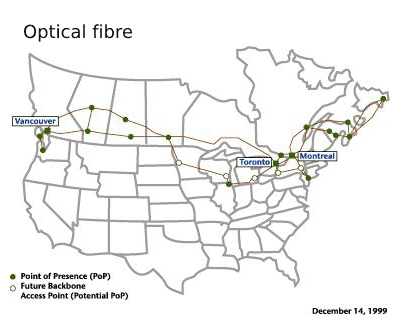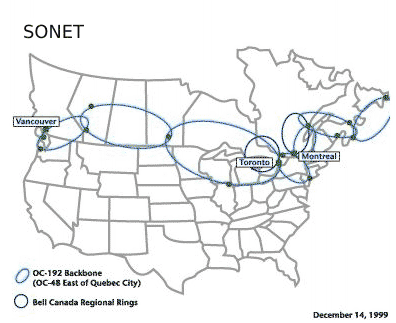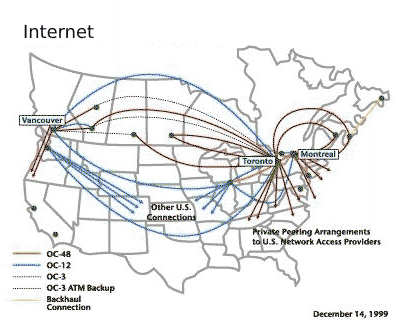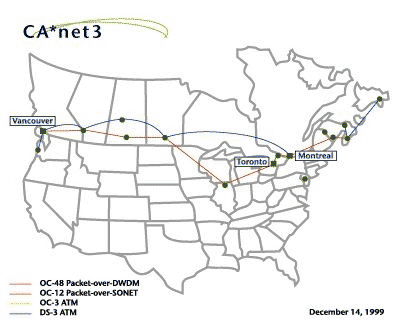
Bell national network

International networks
Wireless
Lower speeds than copper or glass fibre …

 … but very convenient.
… but very convenient.
Spectrum allocations
Protocols
- WAP - Wireless Application Protocol, for `third-generation' mobile
telephony. Designed to hand off connections seamlessly as user moves.
- Bluetooth.
Inexpensive, relatively slow at < 1 Mbit/s, range 10 m.
Based on IEEE 802.11 standard, uses unlicensed 2.4-GHz band.
Emphasis on ‘dynamically handling mobile
units of various kinds'’.
- Wi-Fi. Up to 11 Mbits/s.
Based on IEEE 802.11b standard, uses unlicensed 2.4-GHz band.
Some say
it's a good thing that if people put their base stations in their
windows, then anyone nearby could use them to access the Internet;
this might also become a security problem.
Invisible computing

AKA ‘pervasive computing’.
Combination of small powerful processors and wireless connectivity.
Example application:
tracking belongings and providing reminders.
M. Lamming & D. Bohm,
Computer, 2003 June
![]()
Drawing from
Rensselaer Alumni Magazine, 2004 Summer
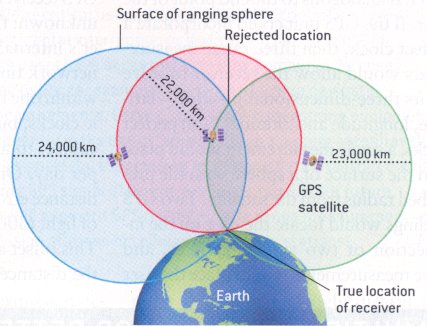
GPS
|
| Sci. Am., 2004 May
|
First GPS satellite launched for military use in 1978.
Requires line of sight to multiple satellites.
Accuracy of 5 to 10 m.
Improving coverage and accuracy.
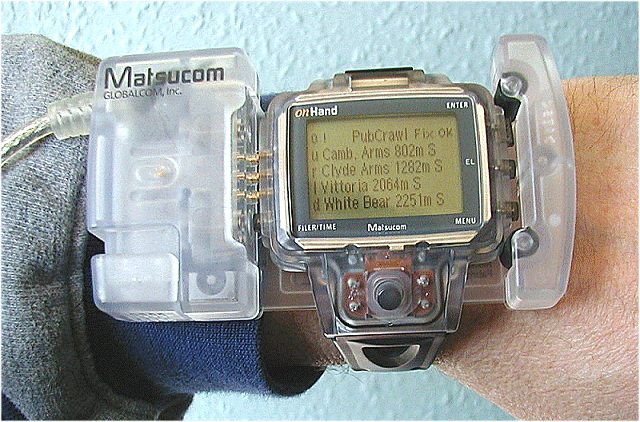
GPS receivers can be mounted in cell phones, pagers, wristwatches, etc.
Medical applications
- disaster relief
(ref)
- automobile tracking and accident response
- personal location for emergency response
- personal tracking to detect confused wandering
(ref)
possibly including monitoring ambient temperature, etc.
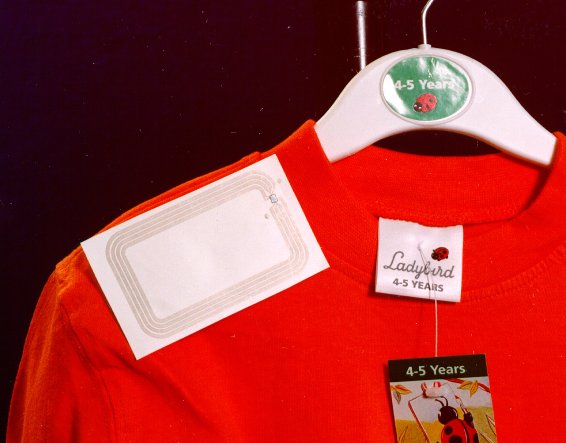
RFID
Inexpensive, powerful.
Reading ranges from centimetres to metres.

Currently at tens of cents/tag, aiming for 1 cent/tag.
Can be used for item-level tagging.
Medical applications
Trauma centre (2004 Apr)
- 2"×¾"×½" RFID tags attached to patient's ankle
as they entered the facility
- 25 RFID readers spread among
3 X-ray rooms, 2 CT-scan rooms, 2 ICU's, an OR and
several general areas
- tag contains 12-byte ID number


ER (2004 Aug)
- ~20 readers
- ~100 credit-card-size tags for patients and staff
- 1"-cube tags for equipment
- short ultrawideband pulses to reduce interference
ER (2006 Mar)
- monitors patient location and vital signs
- ultrasound rather than RF
Cardiology (2007 Mar)
- tags on heart monitors worn by at-risk patients
- patients linked to monitors in database
- location tracked within hospital
MedicAlert (2007 Feb)
- testing with cards
- goal is bracelets

Hospital (2007 Mar)
- ~500 receivers
- ~2000 tags on staff and equipment
- disposable tags on wristbands given to patients upon admission
- e.g., make sure cleaning staff show up quickly after patient discharge
Equipment tracking (2004 Apr)
- 10,000 pieces of medical equipment at
three Virginia hospitals
- location, and whether item is in use, available or in need of servicing
Equipment tracking (2007 Feb)
- nearly 1,000 medical devices in New Orleans
- for use by biomedical engineering and sterilization
- spend less time looking for equipment
Patients and equipment (2007 Feb)
- 23,000 patients/year
- thousands of items, from beds to pumps
- displays OR schedule, and what is actually happening
- plasma-screen display of patient status, for family
- control hoarding of wheelchairs
- make sure devices are regularly inspected and receive software upgrades

Uniforms, OR gowns (2007 Feb)
- tags are sewn into the garments
- employees use personnel badges to open storage closets
- reader inside the closet tracks the closet's contents
- readers also in laundry bins
- savings in inventory space, labor and operational costs
Tracking of high-cost items (2007 Feb)
- supply cabinets with readers for high-cost items
- reduce overstocks and waste
- make sure patients are properly billed

Blood tracking (2006 Feb)
- self-adhesive 1.5×1" RFID label on each bag of blood
- tracked from patient assignment to transfusion
- unique ID number, hospital tracking number used by
blood bank system, and blood type
- match data in patient's bracelet
Medicine tracking (2007 Feb)
- patent filed for digestible tags
- verifying proper drug usage, monitoring drug interactions,
controlling dosage, maintaining inventory control
Manufacturers (2007 Mar)
Drug tracking to fight counterfeiting and diversion:
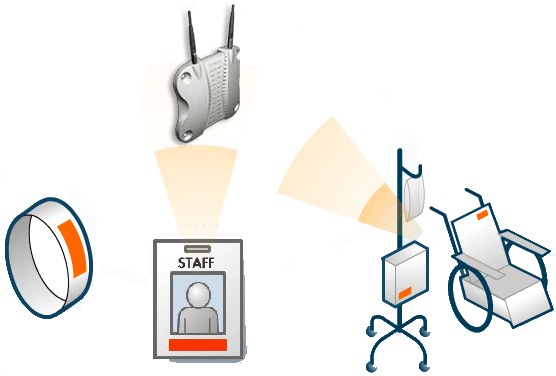
Reducing medical errors (2004 May)
- passive tags on patient bracelets
- active tags on staff ID badges
- tags on equipment
- positive identification of patients
- staff carry wireless PDA's or tablet PC's
- system can detect proximity of staff to patient and automatically
download patient's records

VeriChip
implantable RFID chip: cleared by U.S. FDA for medical applications,
not regulated.
Contains an ID number which provides
access to subscriber-supplied information in a password-protected
Web-based registry.

(Foster & Jaeger, IEEE Spectrum, 2007 Mar)
Privacy concerns


R. Funnell
Last modified: Tue, 2007 Mar 20 17:56:43
 Networks
Networks Networks
Networks


 But if several segments fail at the same time ...
But if several segments fail at the same time ...









 … but very convenient.
… but very convenient.












