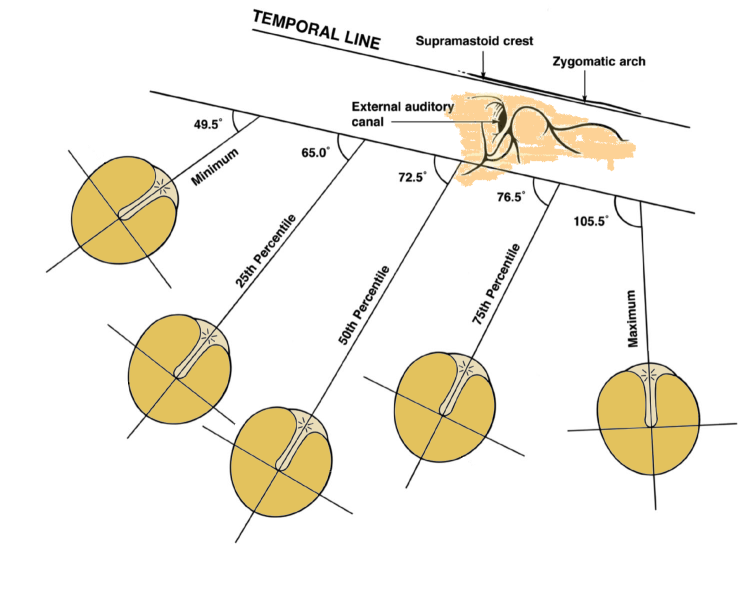
Todd W (2005): Orientation of the manubrium mallei: Inexplicably widely variable. Laryngoscope 115: 1548-1552
Anatomical variability.
For example, orientation of manubrium in human.
Todd NW (2005): Orientation of the manubrium mallei:
Inexplicably widely variable. Laryngoscope 115:
1548–1552
BMDE-501
Modelling
middle-ear mechanics
Slide show generated from me_saf.html by Weasel 2024 Oct 21