 Objectives of middle-ear research
Objectives of middle-ear research Objectives of middle-ear research
Objectives of middle-ear research
© Joe Kohl
ENT = Ear, Nose & Throat = Oto(rhino)laryngology


Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2019 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. J Early Hear Detect Interv. 2019;4(2):1-44. doi:10.15142/FPTK-B748


Probst R, Grevers G & Iro H (2006) Basic otolaryngology: A step-by-step learning guide, Thieme, New York, NY
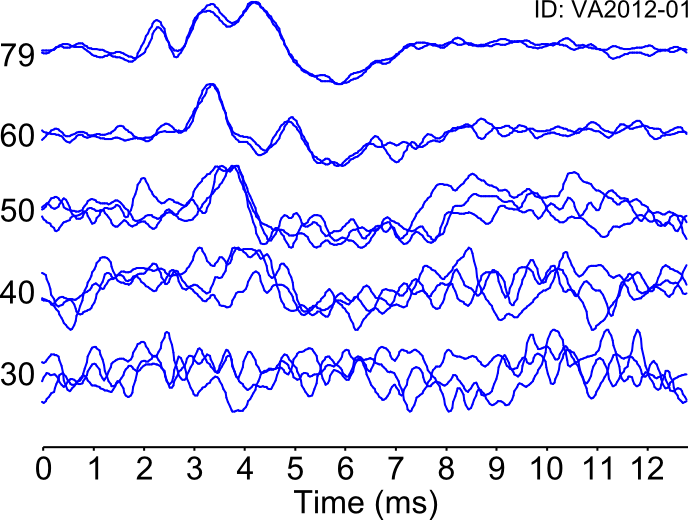
Threshold determination requires judgement about when waves disappear
Olubunmi V. Akinpelu, McGill University, 2013

|
| Diagram of OAE measurement |

Comparison of distortion-product amplitude to noise level
Automated OAE and ABR screening can detect hearing loss,
but they cannot effectively distinguish between
Large numbers of false positives
Due to conditions in middle ear
| Input admittance of electrical circuit = I/V |
| Electrical | Mechanical | Acoustical |
|---|---|---|
| voltage | force | pressure |
| current | velocity | vol. velocity |
| resistor | dashpot | mesh |
| inductor | mass | tube |
| capacitor | spring | volume |

|
| Diagram of admittance measurement |
After Cull (1989): The Sourcebook of medical illustration, Parthenon, Carnforth, xxiii+481 pp.

|
| Diagram of a tympanometer |
Addition of static pressures
but ...
After Cull (1989): The Sourcebook of medical illustration, Parthenon, Carnforth, xxiii+481 pp.
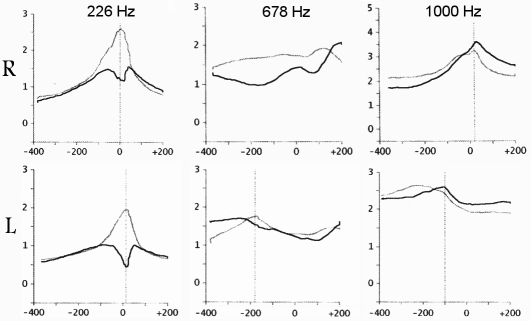
|
|
Tympanograms from 156-day-old infant for three frequencies
Right ear (top) was normal, left ear (bottom) had middle-ear effusions
and failed hearing screening test Dark lines = susceptance, light lines = conductance Units for horizontal axes (static pressure) = daPa, vertical axes = mmho |
In this example

Repair or replacement of the eardrum and ossicles
After Cull (1989): The Sourcebook of medical illustration, Parthenon, Carnforth, xxiii+481 pp.

Smith + Nephew catalogue
Many different designs
Potential technology is increasingly sophisticated:

but
Little systematic analysis of mechanical performance
E.g.,
Slater PW, Rizer FM, Schuring AG & Lippy WH (1997): Practical use of total and partial ossicular replacement prostheses in ossiculoplasty. Laryngoscope 107: 1193-1198
Stupp CH, Dalchow C, Grun D, Stupp HF & Wustrow J (1999): Titan-Prothesen im Mittelohr. 3-Jahres-Erfahrungsbericht. Laryngo- Rhino- Otologie 78(6): 299-303
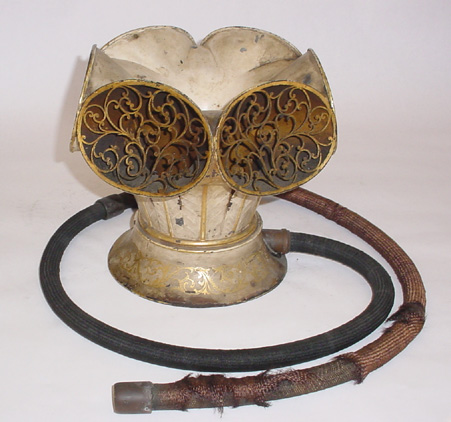

F. C. Rein, ca. 1810
©2005-2009 Washington University School of Medicine, Bernard Becker Medical Library
See also
The History of Hearing Aids (IEEE, 2013)
Design and evaluation of active devices
See also
The History of Hearing Aids (IEEE, 2013)
Characterization of stimulus to inner ear
For interpretation of cochlear experiments
Often, the input to the cochlea is characterized by measuring
After Cull (1989): The Sourcebook of medical illustration, Parthenon, Carnforth, xxiii+481 pp.
Teaching of middle-ear anatomy and surgical techniques:
Can teach using
BMDE-501
Modelling
middle-ear mechanics