The eigenvalues of
\(\mathbf K \mathbf u = \omega^2 \mathbf M \mathbf u\)
correspond to the squares of the natural frequencies,
and the eigenvectors correspond to the associated modes of vibration.
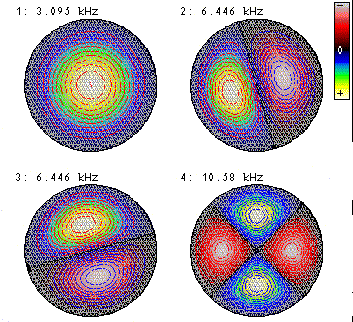
Note the two degenerate modes at 6.446 kHz.
R. Funnell Last modified: 2018-11-07 12:52:06
Slide show generated from fem.html by Weasel 2018 Nov 7