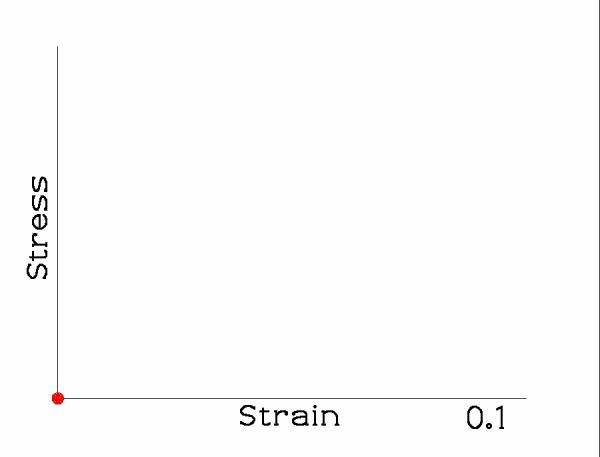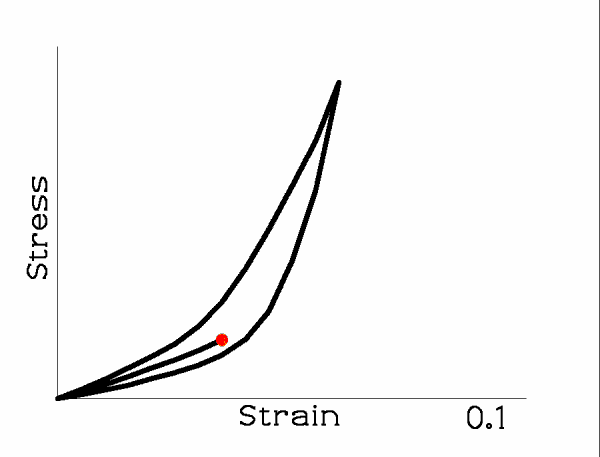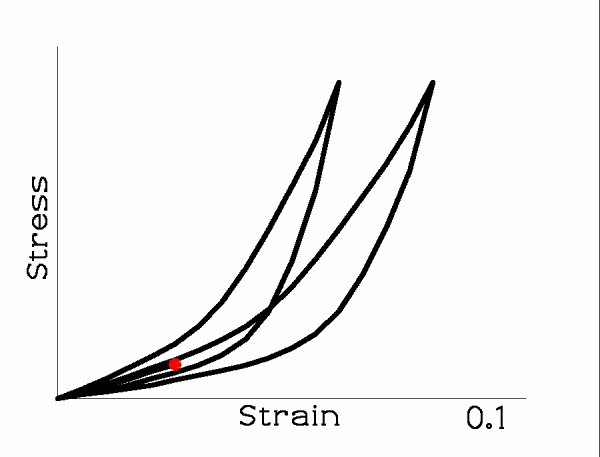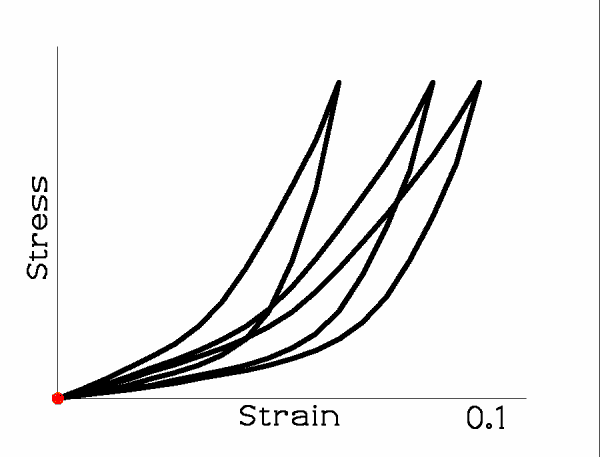
When the tissue is loaded and unloaded repeatedly, the loop shifts.
The loop tends to converge to a fixed form but may take many cycles to do so. Once the loop is unchanging, the tissue is said to have been ‘preconditioned’. If the nature of the cyclic loading is then changed, the preconditioning must be done again.
Modellers seldom attempt to model this phenomenon,
but it may be important in the ear.